gulp是什么
我们来看官网给出的解释:
Automate and enhance your workflow
翻译过来就是:用自动化构建工具增强你的工作流程!
gulp是前端开发过程中对代码进行构建的工具,是自动化项目的构建利器;它不仅能对网站资源进行优化,而且在开发过程中很多重复的任务能够使用正确的工具自动完成;使用它,我们不仅可以很愉快的编写代码,而且大大提高我们的工作效率。
gulp能用来做什么
- 搭建web服务器
- 使用预处理器Sass,Less
- 压缩优化,可以压缩HTML、css、JavaScript、 图片
- 自动将更新变化的代码实时显示在浏览器
- 前端测试
- ……
gulp有极丰富的插件来帮助我们实现各种功能
gulp插件地址:http://gulpjs.com/plugins
安装gulp
前提假设我们已经安装了node,并且对npm也了解
全局安装gulp
全局安装gulp目的是为了通过它执行gulp任务
|
|
查看是否正确安装,我们在终端输入gulp -v
|
|
出现版本号,说明正确安装
新建package.json文件
首先我们先新建一个项目文件夹
|
|
然后进入项目文件夹
|
|
创建一个package.json
|
|
在项目目录里局部安装gulp
|
|
创建gulpfile.js
在根目录下面创建gulpfile.js文件,此文件为配置文件
自定义任务
gulpfile.js
|
|
然后在命令行执行gulp任务
|
|
我们会看到打印出了”Hello World”
默认任务
gulpfile.js
|
|
这样我们就可以直接gulp了
|
|
Basic
读取想要处理的文件,然后把处理好的文件放到指定的地方
gulp.src()
gulp.src()方法可以帮我们找到想要处理的文件
.pipe()
然后通过.pipe()来处理这些找出来的文件,pipe就是一个管道,每一个管道里面我们都可以指定它的功能来处理这个文件
.pipe(gulp.dest())
最后我们再使用.pipe(gulp.dest())方法,去把处理好的文件放到指定的地方。
dest is short for destination(目的地,目标位置)
Copy
目录结构
|
|
gulpfile.js
|
|
然后在命令行执行gulp copy
|
|
然后目录结构就变了
|
|
glob
目录结构
|
|
下面我们要做的就是把jpg图片复制到dist目录下的images文件夹里
gulpfile.js
|
|
执行gulp images
|
|
然后我们观察目录结构变化
|
|
那么怎么才能把png和jpg都复制过来呢?
gulpfile.js
|
|
执行gulp images后,dist文件夹目录结构如下
|
|
我们再来看,修改一下
|
|
|
|
如果想要深层次匹配
|
|
怎么样,images里的文件全都匹配过来了
多个glob
目录结构
|
|
gulpfile.js
|
|
执行gulp data
dist的目录结构变为
|
|
negate
不想包含的文件用!排除
例如json文件夹里
|
|
我们不想要negate开头的json文件
gulpfile.js
|
|
执行完过后,就不会复制negate-01.json这个文件了
任务依赖
如果一个任务的建立是依赖于其他任务,就需要用到以下的写法
gulpfile.js
|
|
然后执行gulp build
|
|
我们可以看出,copy,images和data三个任务是同时进行的,然后再执行build任务
watch
用gulp.watch()方法可以监视文件的变化
gulpfile.js
|
|
执行gulp watch就可以监视文件的变化
plugin
gulp提供了很好的接口,它本身并不会去做太多的事情,除了去可以读取文件,监视文件的变化,可以把文件放到指定的位置,我们可以插件来扩展gulp的功能,这些插件可以取执行特定的任务,比如说:
- 编译Sass,编译Less
- 合并文件
- 压缩、混淆文件
- 重命名
- 优化图像的尺寸
- 创建一个本地的开发服务器
- …
gulp插件地址:[http://gulpjs.com/plugins
使用方法都类似
- 先找到所需的插件,然后
npm install 插件名 --save-dev安装 - 然后在gulpfile.js中引入插件
const minifycss = require("gulp-minify-css") - 查看插件文档,看使用方法
gulp-sass
安装gulp-sass
|
|
使用gulp-sass
在配置文件gulpfile.js中引入这个插件
|
|
然后执行gulp sass
呃,我们遇到个错误
|
|
在Stack Overflow上查了一下,说让我们运行一下npm rebuild node-sass
于是我们执行npm rebuild node-sass
然后再执行gulp sass
还是不行,于是我们在https://github.com/sass/node-sass/releases/tag/v3.13.1里看到了
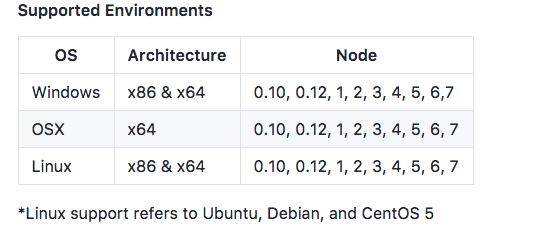
想起来我装的是node的最新版,输入node -v
|
|
也罢,那就等着它支持到8.x了吧。
于是,我们假装成功了(不要脸.jpg)
然后我们就能看见在dist文件夹下有一个css文件夹,里面有style.css文件
gulp-less
安装gulp-less
|
|
使用gulp-less
在配置文件gulpfile.js中引入这个插件
|
|
然后执行gulp less
|
|
会在dist下面生成
|
|
gulp-connect
安装gulp-connect
|
|
使用gulp-connect
将gulp-connect模块导入
|
|
然后执行gulp server,我们会看到如下信息
|
|
告诉我们在http://localhost:8080就可以查看网页了
reload
当某些文件变化以后,能实时地刷新页面,这样就不用每次修改之后,再手动地刷新页面来查看变化。
打开gulpfile.js,找到创建服务器的任务,把livereload的值设置为true
|
|
执行顺序是
- index.html文件发生变化
- 触发watch任务
- watch任务又触发copy任务
- 将更改后的index.html拷贝到dist文件夹中
- reload
gulp-concat
使用gulp-concat这个插件我们可以使几个文件合并到一块儿
安装插件
|
|
使用gulp-concat
|
|
合并后的dist目录
|
|
gulp-uglify
把几个js文件合并到一块儿,接下来我们可以再压缩混淆一下,完成这个动作我们可以使用gulp-uglify这个插件
安装插件
|
|
使用插件
|
|
然后执行gulp scripts就可以压缩混淆了
注意:
若出现一下种错误,说明js代码有问题
|
|
rename
在把处理好的文件存储到指定的位置之前,我们可以重命名一下它,这里使用gulp-rename这个插件
安装插件
|
|
使用插件
|
|
这个就不一一解释了
gulp-minify-css
压缩css使用gulp-minify-css
安装插件
|
|
使用插件
|
|
执行gulp less就可以压缩css代码了
gulp-imagemin
gulp-imagemin可以帮我们优化图片的尺寸,在保证不改变图像质量的情况下可以让图像的体积变得更小一些,下面我们先去安装一下这个插件
安装插件
|
|
使用插件
|
|
然后执行gulp images就可以执行了。
本文结束,感谢阅读。
本文作者:melody0z
本文链接:https://melodyvoid/gulp/gulp-learning-notes.html
欢迎转载,转载请注明文本链接

